Introduction to AI/ML
Gain a foundational understanding of artificial intelligence and machine learning, their differences, types, and practical use cases in fields like transportation, medicine, and software development. Learn how AI and ML impact DevOps and explore simple Python examples for training models.
faqOver the past two and half years, I’ve had the opportunity to invest much of my time in data science, machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI). This blog post answers many of the questions I recount having prior to learning about the work, techniques, jargon, and tooling in ML and AI.
What is AI and ML?Artificial Intelligence is a technique for building systems that mimic human behavior or decision-making.
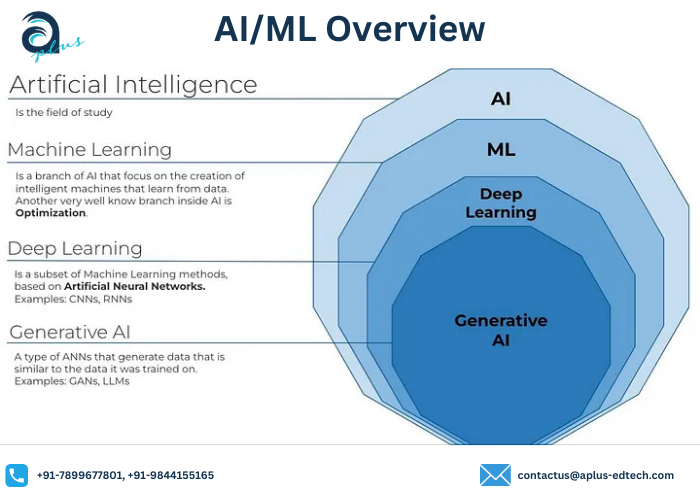
Machine Learningis a subset of AI that uses data to solve tasks. These solvers are trained models of data that learn based on the information provided to them. This information is derived from probability theory and linear algebra. ML algorithms use our data to learn and automatically solve predictive tasks.
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning which relies on multilayered neural networks to solve these tasks. Forms of Machine LearningGiven that machine learning is a fundamental basis for AI, it’s worthwhile to understand the different forms of machine learning.
There are three kinds of machine learning: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Each form solves problems differently.
Supervised Machine LearningIn supervised machine learning, we know about the data and the problem. Think of it as, “given a set of features x, we know the value of y,” and so in supervised learning, we create a function that approximates results based on some set of data.
There are two kinds of supervised learning: classification and regression. In a classification problem, we assign data to categories. For example, given a client’s medical information, they test positive or negative for diabetes. In classifications, our trained models, known as classifiers, classify data points into different groups.
If we instead wanted to solve a different problem, like predicting the future value of GameStop stock given the stock market history, we’d turn to a regression. In regression, we return numerical values. Given some sentences, this is the percent likelihood the person is happy or sad.
Unsupervised Machine LearningIn unsupervised machine learning, our data is unlabelled. There are two forms of unsupervised machine learning: clustering and dimension reduction.
In clustering, we learn more about data points as they are clustered, or grouped together. This allows learned models to understand a data set, detect anomalies, and assign relationships between points, often allowing users to develop new categories or features about the data set.
In dimension reduction, we plot data points across different dimensions and feature sets to understand our data sets. This allows for techniques like feature selection or transformation. Dimension reduction solves the curse of dimensionality. The more features to a data set, the more data is needed, and processing many noisy features can impact the performance of an ML model, so unsupervised machine learning techniques are often paired with supervised or reinforcement learning algorithms.
Reinforcement LearningIn reinforcement learning (RL), we are learning models over time. A common technique is to utilize deep learning with reinforcement learning to derive relationships between features of a data set that may not otherwise be solved through human research. Deep learning RL has been very successful in the field of medicine as of late.
Quick Enquiry
Message
Get in Touch Now!
Contact Us
Head Office
:
APLUS EdTech
# 87/1, Site No: 1,
Subhasha Nagara, Battarahalli,
Salarpuria Celesta Apartments,
TC Palya Main Road,
Krishnarajapuram, Bangalore – 560 049.
Phone: + 91-7899677801,+
91-9844155165
Locate on Google Map
Branch:
122, Sri Nivasa Reddy Layout, AECS Layout, Marathahalli, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560037
Phone: +91 91082 49111 / (080) 4865 8559
Email: contactus@aplus-edtech.com
Address: Bengaluru, India
Locate on Google Map
